CGT Global is looking for blood and bone marrow donors to take part in life-saving medical research. Join us in supporting scientists around the world by becoming a CGT Global partner!
Why Are Blood Donors Important?
Blood and bone marrow donors are an important part of the research process
Researchers worldwide are developing new treatments and cures for significant medical conditions including cancers, rare childhood diseases, and autoimmune disorders. To do this important work, scientists need human cells during the research and development process to fully understand how their treatments and cures will respond in the human body. Blood and bone marrow donations from people like you can provide researchers with the cells they need to ensure their treatments are safe and that they really work!

Your donation with CGT Global could help researchers find treatments and cures for significant diseases like the ones listed below! Click on an image to learn more about the disease
Scientists utilize unique components of human blood and bone marrow, in an effort to find treatments and cures for a multitude of medical conditions. Here at CGT Global, we streamline this process to provide these researchers with the exact samples they need. Take a moment to read about the ways you can donate and what’s involved.
White blood cells are one of the four components of whole blood. A white blood cell collection procedure is called apheresis (ay-fer-ee-sis). Apheresis is the process of drawing blood, filtering out parts of the blood through a cell-separating machine, and then returning the blood back to the donor. The process can take between 4-6 hours and donors are able to resume their regular activities after donating! Apheresis collections can be used for research and development and in some cases is used to treat blood cancers through allogeneic and autologous treatments.
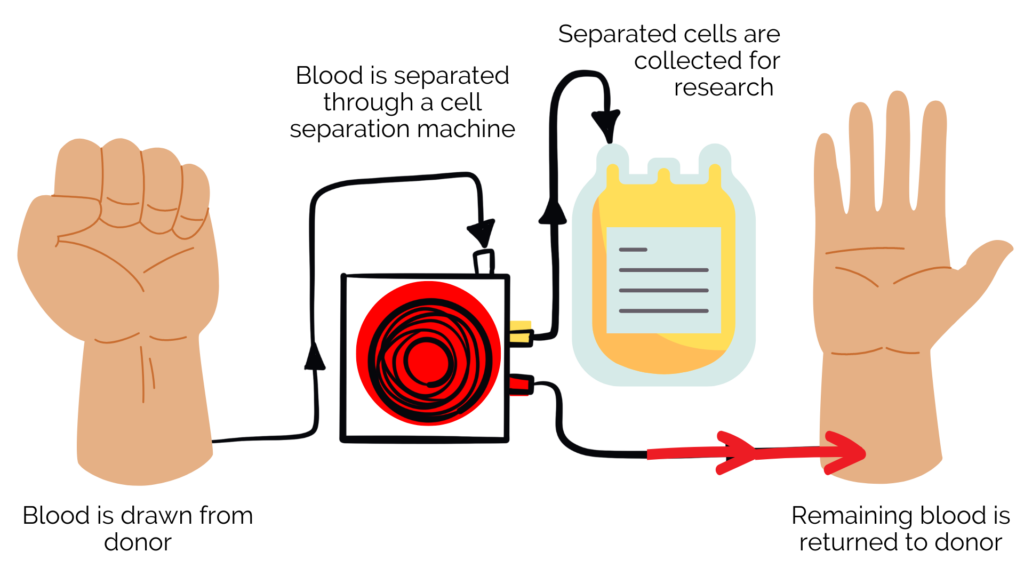
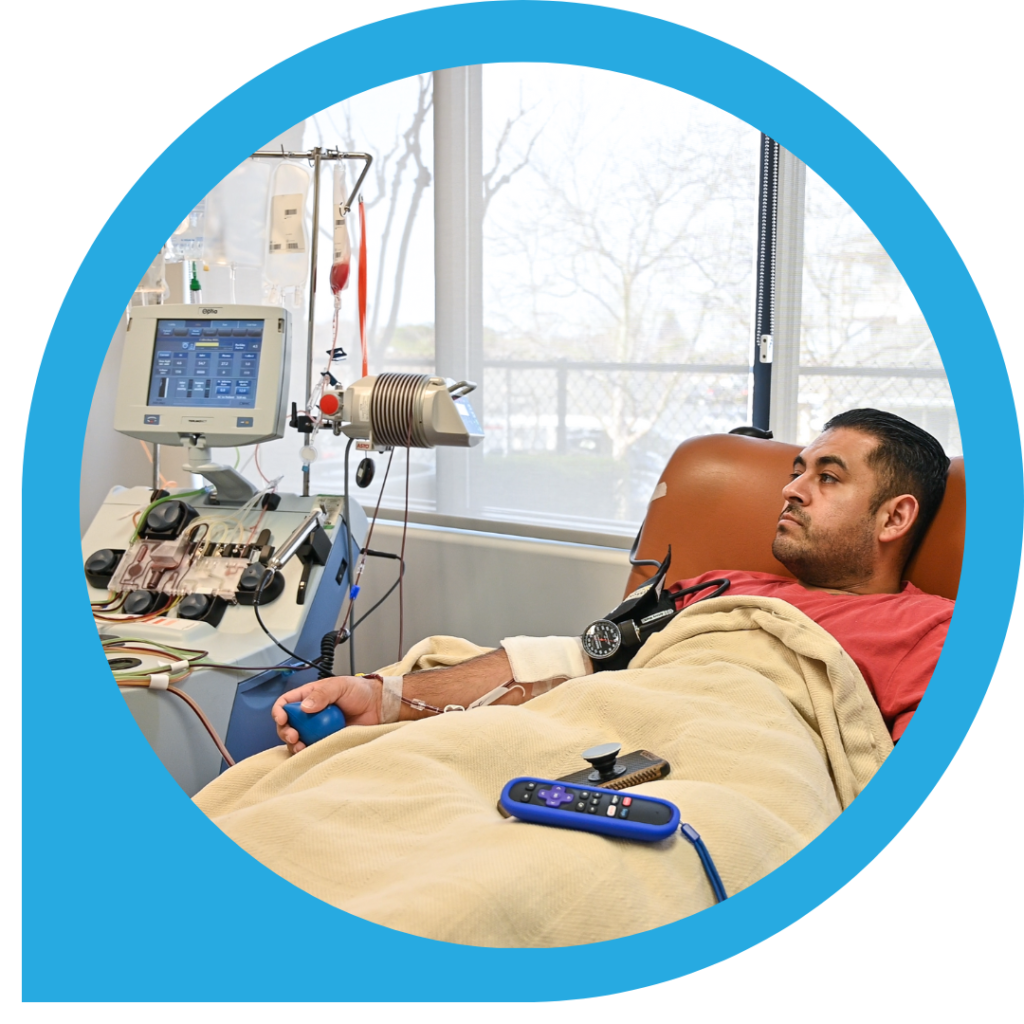
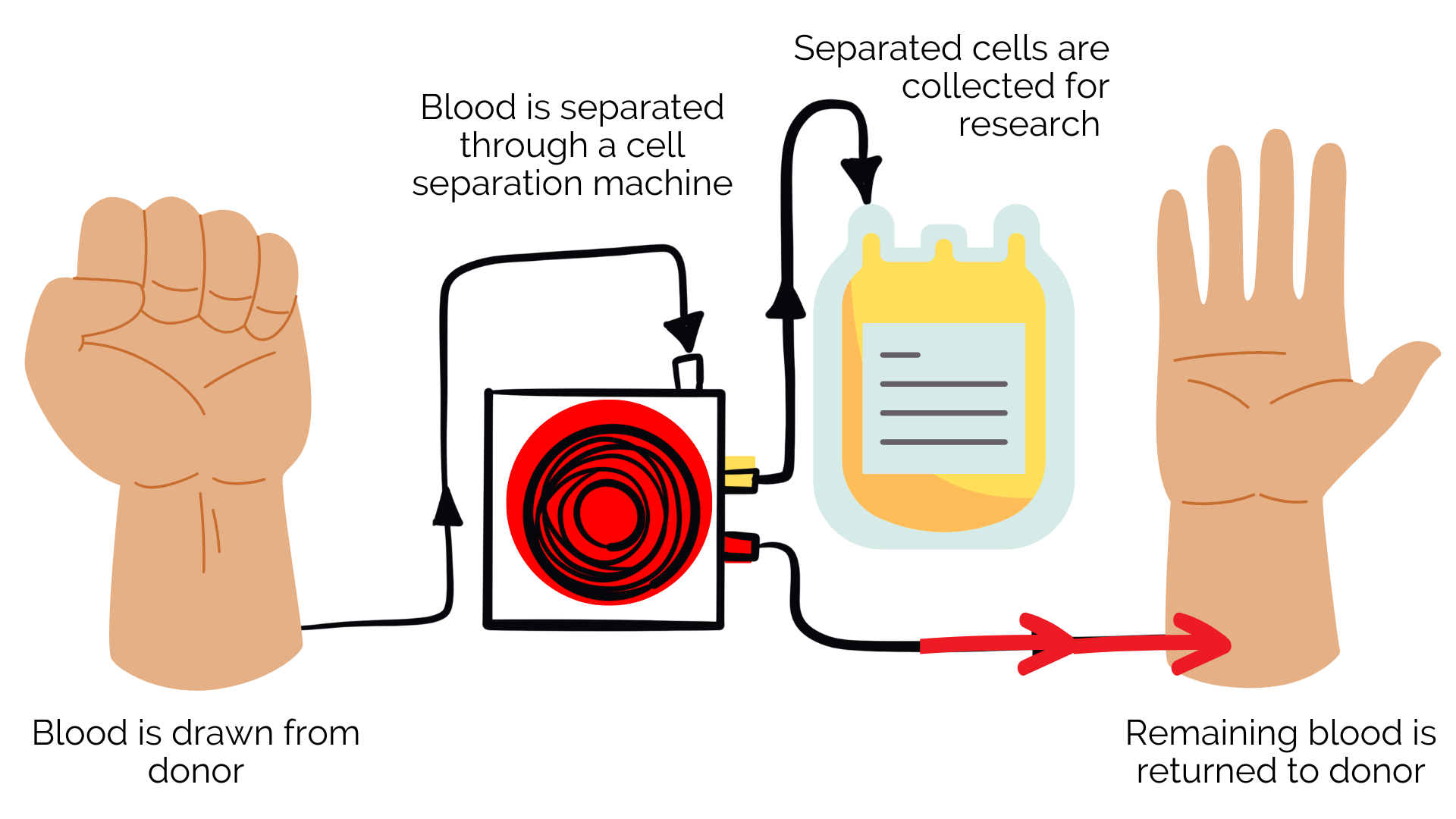
How it works: In order to qualify for apheresis, you must have large veins in both arms. You will be seated in a chair in a comfortable position and a sterile needle will be inserted into each arm. Your blood will be drawn from one arm and pass through the apheresis machine. The machine will separate the white blood cells and plasma and collect them in a bag.
The remaining components of your blood will be delivered back to you in your other arm. Please be aware that since the needles remain in your arm for the entire procedure, you cannot bend your arms for the length of the donation. If you need assistance (or even need your nose scratched!) you can always ask a CGT Clinic staff member. We are here to help! You will have a TV with wireless headphones and cable or Netflix to pass the time.
Time: A white blood cell collection takes between 4 to 6 hours. Please be aware that if the procedure is interrupted, you cannot be reconnected to the machine, and you may not be eligible for the entire amount of the compensation. Gaps between white blood draws must be at least 4 weeks.
Compensation: You will be compensated $150 for your apheresis (white blood cell) appointment.

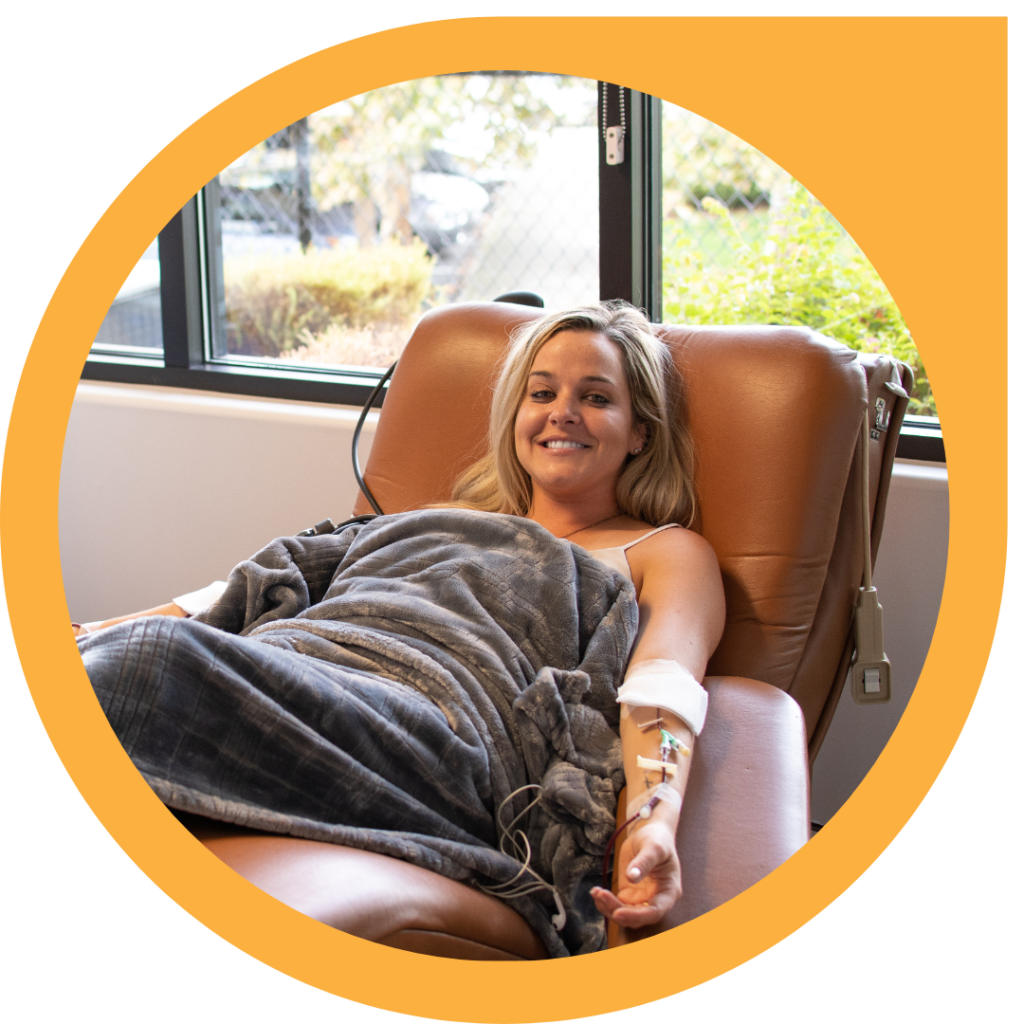
Whole blood donations are the most common type of blood donation. During a whole blood donation, the blood with all of its parts is drawn from a vein in the donor's arm. Whole Blood donations are the quickest type of donations. This short amount of time makes a huge difference to scientists around the world who need whole blood for their important research.
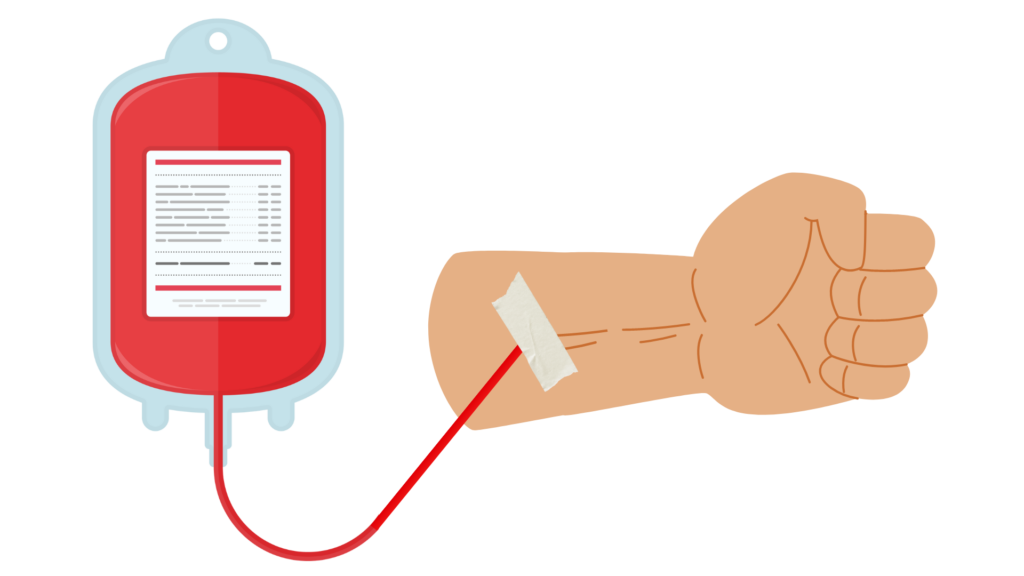

How it works: A whole blood donation is a simple blood draw. A phlebotomist will insert a sterile needle into your arm and collect the blood in a blood bag or in tubes.
Time: Whole blood donations can take anywhere from 30-90minutes depending on the size of donation given. A small donation (under 100mL) usually takes about 30-60minutes, while a larger donation may take closer to 45-90minutes. This includes time for paperwork as well as the donation itself.
Compensation: You will be compensated $50 for a small blood draw appointment and $100 for a large draw appointment.

Bone marrow donations are vital for important research. Bone marrow is packed with valuable cells that give rise to the blood that flows through your body! The procedure is quick, and our experts make sure that it's as comfortable and painless as possible.
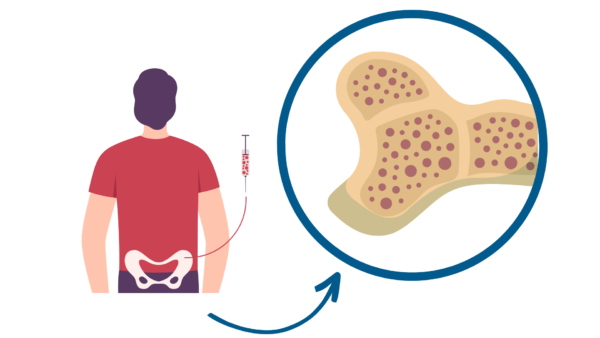

How it works: Bone marrow donations may seem a bit scary, but they are actually relatively quick and generally very tolerable. A licensed healthcare provider will perform the procedure. You will lie on your stomach on the exam room table and a local anesthetic will be applied to numb the donation area. The bone marrow will be extracted from your iliac crest (hip) on either side. During the withdrawal of the bone marrow (called aspiration), you may feel a brief pinching sensation. When the draw is complete, you should not experience any impairment to your normal functioning, and should be safe to drive home.
Time: The Bone Marrow appointment takes 25-30 minutes. Plan to spend 1-2 hours in the collection center.
Compensation: You will be compensated $250 for your Bone Marrow appointment.
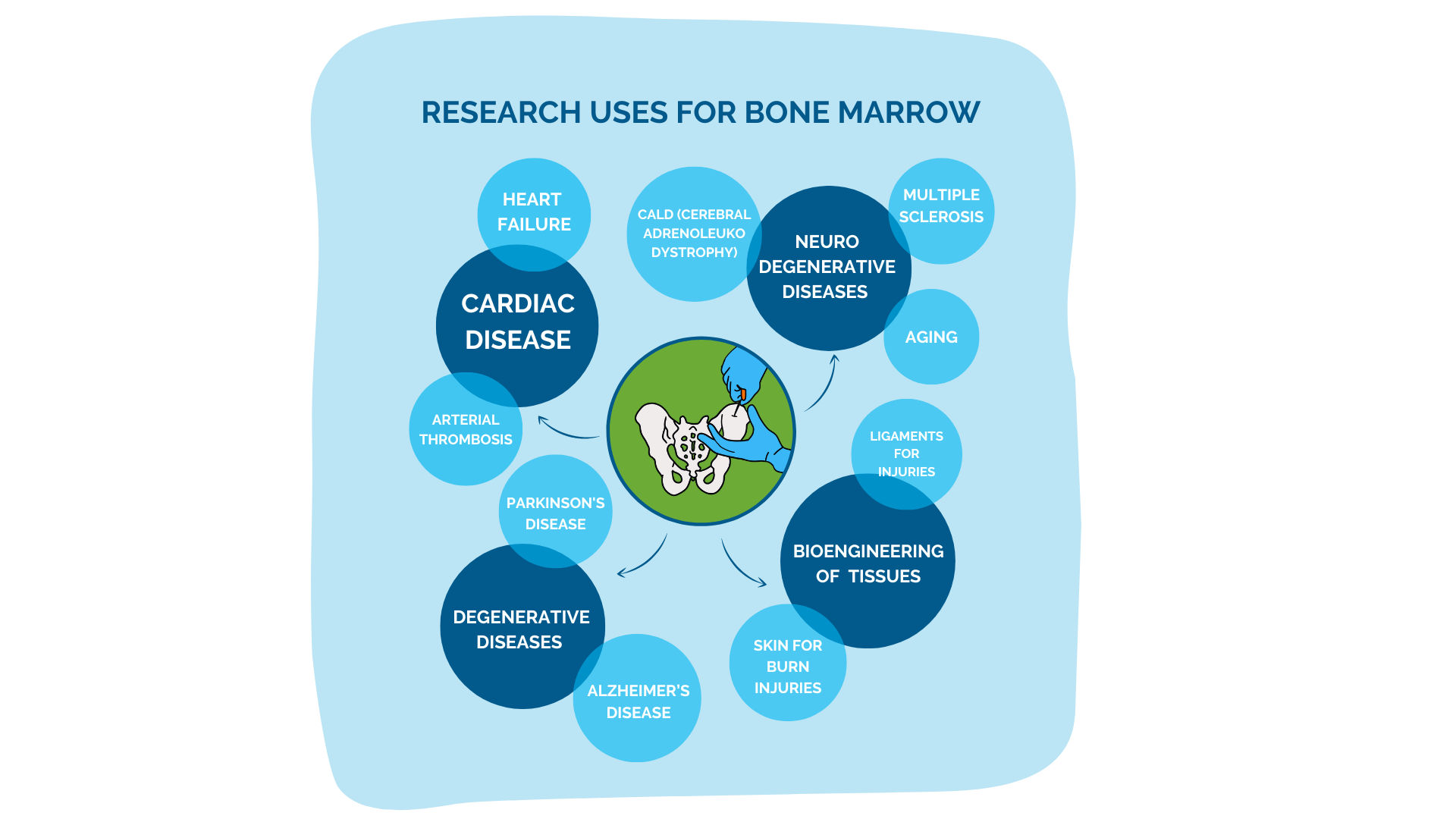
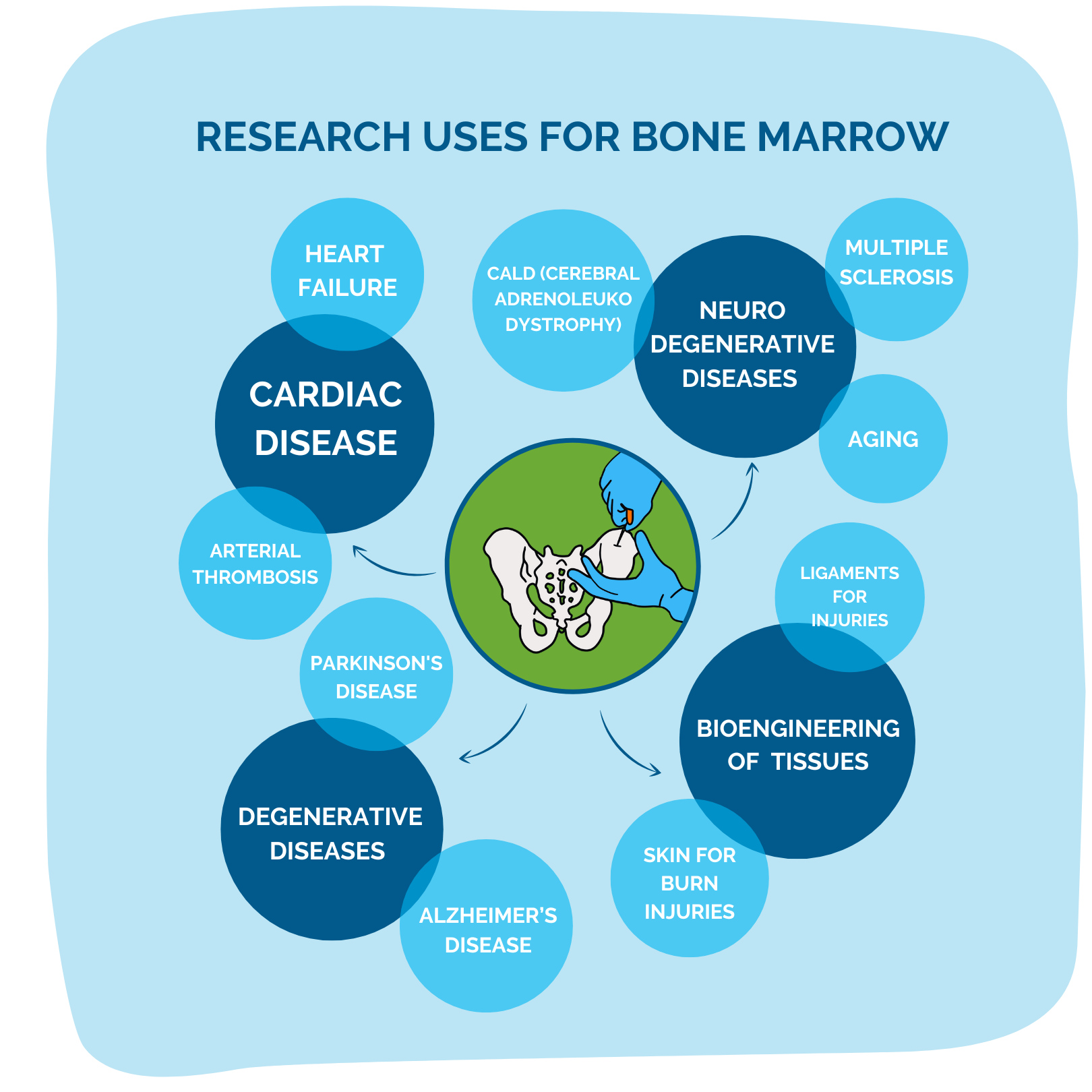

Mobilized blood donations are very important to researchers! Donors who qualify for a mobilized blood donation are injected with a "mobilizing agent" a few days before their donation to SUPERCHARGE their immune cells! These cells are then collected and used by scientists worldwide searching for treatments and cures for some of the most challenging diseases.
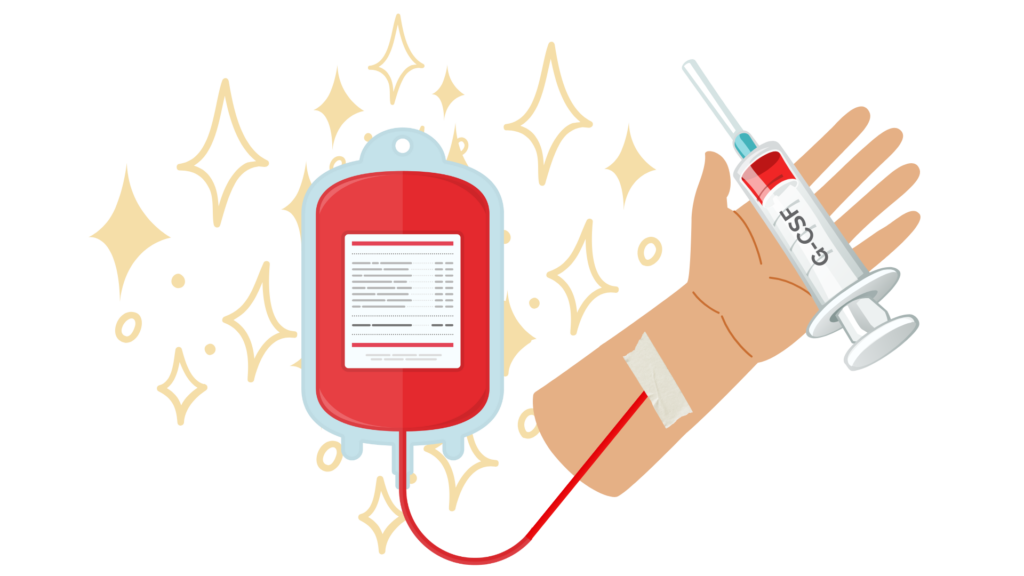

How it works: A mobilized white blood cell collection is a special kind of white blood cell appointment where you will receive injections of a “mobilizing agent,” (G-CSF, a drug which boosts your body’s white blood cell production) before your apheresis appointment. If you qualify for this procedure, you will be scheduled for up to five days of G-CSF injections prior to your apheresis appointment.
Time: The first G-CSF appointment will take about 60 minutes. The following G-CSF appointments will take approximately 30-60 minutes. The white blood cell collection appointment will take between 4-6 hours.
Compensation: Depending on the project you qualify for and your total number of G-CSF injections, you are eligible for up to $1000.
*Qualified donors are eligible to be mobilized by G-CSF twice in a lifetime. You are able to continue other donations regularly, such as small and large blood draws, after the specified deferral period.

Download our donor nutrition tips here!

Becoming a blood or bone marrow donor has a BIG impact on important research around the world. Understanding the role individual cells play in the human body can help you understand why scientists need them.
Red Blood Cells

Red Blood Cells
Red blood cells seem to get all the attention, and for good reason! They make up over 40% of the blood in your body! Imagine it... there are 150 BILLION red blood cells in ONE OUNCE of blood.
Take a deep breath in, and now take a deep breath out. As you read this, your red blood cells are carrying oxygen from your lungs to all of the tissues in your body, and transporting carbon dioxide to the lungs, where you release it when you exhale. Red blood cells are so important that without them you would - to put it gently - die within minutes.
White Blood Cells
Basophils
Basophils are a type of powerful little immune response cells known as granulocytes. Basophils are responsible for your body's immune response, recognizing foreign invaders in the body and attacking them! Basophils are incredibly important for keeping you healthy and strong, defending the body against allergens, viruses, bacteria, and parasites! Basophils even prevent dangerous blood clotting! Overactive basophils are responsible for asthma - so if you or someone you know suffers from asthma, you now know it's their basophils working overtime.

Eosinophils
Eosinophils are another important immune response granulocyte. Eosinophils play a large role in keeping you healthy by defending the body against allergens, pathogens, and parasites! Have allergies? You can thank basophils AND EOSINOPHILS for that! So the next time you have itchy eyes on a beautiful spring day, you can lovingly tell your eosinophils "chill out!"

Neutrophils
Neutrophils are another immune response granulocyte. Neutrophils are the body's emergency response system when bacteria invade. They are sort of like your body's very own first responders! If you have an infection or a tissue injury, you can count on neutrophils to show up and fight off bacteria... gobbling them up like Pac Man!
Monocytes
Monocytes live in your blood and tissue, and their main role is to find and destroy harmful invaders like viruses, bacteria, and fungi (not to be confused with "fun guys"). Macrophages fall into two categories - dendrites and macrophages. Macrophage cells surround the invading virus or bacteria and ingest, kill, and remove them from the body. Dendrites are the body's alarm system. When they sense the arrival of an invader, it's their job to call on other immune cells for backup!


Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are amazing defenders of the body. Their main goal is to fight off cancer and foreign viruses and bacteria in the body.
There are two different types of lymphocytes in your body, T cells and B cells. T cells control your body’s immune response and attack and kill cancer cells, infected cells, and tumor cells. B cells make antibodies to target viruses, bacteria, and other invaders. Lymphocytes are the most important warriors in the fight against cancer.
Platelets
Platelets
Have you ever had a nosebleed? While stuffing tissue up there might seem to do the trick, the real reason your nose stopped bleeding was platelets! Platelets are the body's tourniquet. Whenever you sustain an injury or start bleeding, platelets band together to form a clot which stops excessive blood loss. So thank your platelets, because without them, even the smallest cut could be very dangerous.
Stem Cells
Stem Cells
From you, all cells form
endless possibility
new life, new healing
Yes. We love stem cells so much that we wrote a haiku about them. But can you blame us? Stem cells are AMAZING. They are the cells that give rise to every other cell in your body, and if that's not worth a poem, we don't know what is.
Two important types of stem cells are pluripotent and multipotent. Don't let the fancy scientific names scare you. This just means one type of stem cell (pluripotent) can become any type of cell in the body, and the other type (multipotent) develops into mostly one type of specialized cell. Researchers are interested in stem cells because their versatility presents endless opportunities!
Bone Marrow
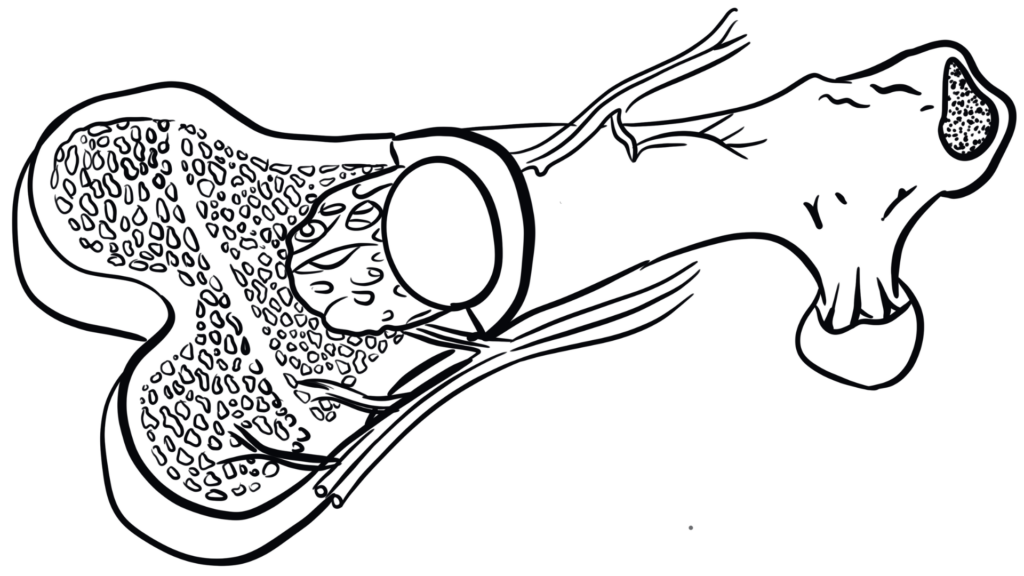
Bone Marrow
Bone marrow is a spongy material inside your bones loaded with very important stem cells. These stem cells produce red bone marrow and yellow bone marrow. Red bone marrow creates red and white blood cells (you learned about those above!) AND platelets which keep your blood from clotting. Yellow bone marrow is mostly made up of fat and stem cells that produce the bone and cartilage in your body. When you donate bone marrow, you're really donating all of those important cells that researchers need!
Whole Blood

Whole Blood
Whole blood is all of the blood that flows through your body. It contains all of the red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets and plasma we discussed above. When you donate whole blood, you're donating the whole enchilada! That's pretty impressive.
Quiz Yourself!
Hold your mouse over the question to view the correct answer! (or just view the key below!)



LEARN MORE ABOUT CGT GLOBAL
We are the leading global biospecimen provider of human primary cells, stem cells, bone marrow, cord blood, peripheral blood, and disease-state products
Advancing Medical Breakthroughs

Advancing Medical Breakthroughs
Founded in 2010, we know how important biospecimens are to medical research and how frustrating it can be waiting for samples.
CGT Global is dedicated to accelerating research projects at life-changing speed to aid in the development of new treatments and even cures for patients worldwide.






